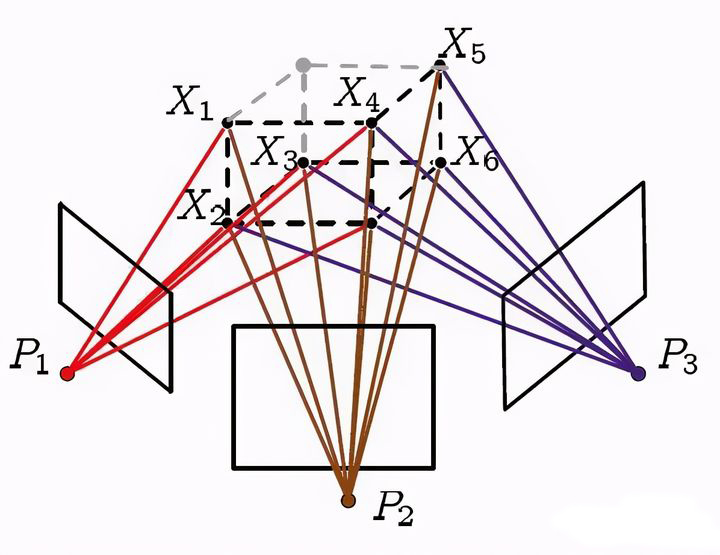
Bundle Adjustment(光束平差法、捆集调整等)是指从视觉重建中计算出最优的 3D 模型和相机参数(内参和外参)。从每个特征点反射出来的几束光线(bundles of light rays),在把相机姿态和特征点的位置做出最优的调整(adjustment)之后,最后收束到光心的这个过程,简称 BA。
本文总结网络资源,对 BA 进行了总结。
Bundle Adjustment Bundle Adjustment(光束平差法、捆集调整等)是指从视觉重建中计算出最优的 3D 模型和相机参数(内参和外参)。从每个特征点反射出来的几束光线(bundles of light rays),在把相机姿态和特征点的位置做出最优的调整(adjustment)之后,最后收束到光心的这个过程,简称 BA。
图-1 BA 示意
假设空间位置的 3D 点为:X = { x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x n } X = \{ x_1, x_2, ..., x_n \} X = { x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x n } P = { p 1 , p 2 , . . . , p m } P =\{ p_1, p_2, ..., p_m \} P = { p 1 , p 2 , . . . , p m } u i u_i u i x i x_i x i K K K s i s_i s i u i u_i u i
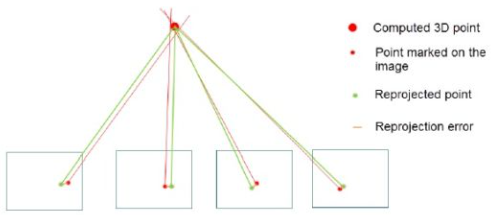
图-2 BA 的计算目标
对于单个相机的 BA,可以构建重投影误差最小二乘如下:
ε ( X , T ) = ∑ i = 1 n ∣ ∣ u i − 1 s i K T x i ∣ ∣ 2 \varepsilon (X, T) = \sum_{i=1}^{n} || u_i - \frac{1}{s_i} K T x_i ||^2
ε ( X , T ) = i = 1 ∑ n ∣ ∣ u i − s i 1 K T x i ∣ ∣ 2
其中,变换矩阵 T T T
T = [ R t 0 T 1 ] ∈ S E ( 3 ) , R T R = I , d e t ( R ) = 1 , t ∈ R 3 T =
\left[
\begin{matrix}
R &t \\
\pmb{0}^T &1
\end{matrix}
\right]
\in SE(3),\
R^T R = I, \ det(R) = 1,\ t \in \mathbb{R}^3
T = [ R 0 0 0 T t 1 ] ∈ S E ( 3 ) , R T R = I , d e t ( R ) = 1 , t ∈ R 3
对于有约束的变换矩阵在最小二乘中不便求解,因此转换为无约束的李群求解:
ε ( X , T ) = ∑ i = 1 n ∣ ∣ u i − 1 s i K ⋅ exp ( ξ ∧ ) ⋅ x i ∣ ∣ 2 \varepsilon (X, T) = \sum_{i=1}^{n} || u_i - \frac{1}{s_i} K \cdot \exp (\xi^{\wedge}) \cdot x_i ||^2
ε ( X , T ) = i = 1 ∑ n ∣ ∣ u i − s i 1 K ⋅ exp ( ξ ∧ ) ⋅ x i ∣ ∣ 2
定义误差函数为:
f ( x i , ξ ) = u i − K ⋅ exp ( ξ ∧ ) ⋅ x i f (x_i, \xi) = u_i - K \cdot \exp (\xi^{\wedge}) \cdot x_i
f ( x i , ξ ) = u i − K ⋅ exp ( ξ ∧ ) ⋅ x i
对于高斯牛顿法,函数 f ( x ) f(x) f ( x )
J ( x ) T ⋅ J ( x ) ⋅ Δ x = − J ( x ) T ⋅ f ( x ) J(x)^T \cdot J(x) \cdot \Delta x = -J(x)^T \cdot f(x)
J ( x ) T ⋅ J ( x ) ⋅ Δ x = − J ( x ) T ⋅ f ( x )
仅需要求 f ( x i , ξ ) f(x_i, \xi) f ( x i , ξ )
优化相机内参及畸变系数,相机的位姿(6dof)和 landmark 代价函数写法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 template <typename CameraModel>class BundleAdjustmentCostFunction {public : explicit BundleAdjustmentCostFunction (const Eigen::Vector2d& point2D) :observed_x_(point2D(0 )), observed_y_(point2D(1 )) { } static ceres::CostFunction* Create (const Eigen::Vector2d& point2D) return (new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction< BundleAdjustmentCostFunction<CameraModel>, 2 , 4 , 3 , 3 , CameraModel::kNumParams>(new BundleAdjustmentCostFunction (point2D))); } template <typename T> bool operator () (const T* const qvec, const T* const tvec, const T* const point3D, const T* const camera_params, T* residuals) const T projection[3 ]; ceres::UnitQuaternionRotatePoint (qvec, point3D, projection); projection[0 ] += tvec[0 ]; projection[1 ] += tvec[1 ]; projection[2 ] += tvec[2 ]; projection[0 ] /= projection[2 ]; projection[1 ] /= projection[2 ]; CameraModel::WorldToImage (camera_params, projection[0 ], projection[1 ], &residuals[0 ], &residuals[1 ]); residuals[0 ] -= T (observed_x_); residuals[1 ] -= T (observed_y_); return true ; } private : const double observed_x_; const double observed_y_; };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 ceres::Problem problem; ceres::CostFunction* cost_function = nullptr ; ceres::LossFunction * p_LossFunction = ceres_options_.bUse_loss_function_ ? new ceres::HuberLoss (Square (4.0 )) : nullptr ; cost_function = BundleAdjustmentCostFunction<CameraModel>::Create (point2D.XY ()); problem_->AddResidualBlock (cost_function, p_LossFunction, qvec_data, tvec_data, point3D.XYZ ().data (), camera_params_data);
优化相机内参及畸变系数,pose subset parameterization(pose 信息部分参数优化)和 3D landmark,当只优化姿态信息时,problem 需要添加的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 map_poses[indexPose] = {angleAxis[0 ], angleAxis[1 ], angleAxis[2 ], t (0 ), t (1 ), t (2 )}; double * parameter_block = &map_poses.at (indexPose)[0 ];problem.AddParameterBlock (parameter_block, 6 ); std::vector<int > vec_constant_extrinsic; vec_constant_extrinsic.insert (vec_constant_extrinsic.end (), {3 ,4 ,5 }); if (!vec_constant_extrinsic.empty ()) { ceres::SubsetParameterization *subset_parameterization = new ceres::SubsetParameterization (6 , vec_constant_extrinsic); problem.SetParameterization (parameter_block, subset_parameterization); }
优化相机内参及畸变系数,pose subset parameterization(pose 信息部分参数优化)和 3D landmark,当只优化位置信息时,problem 需要添加的代码如下(同上,只需修改一行):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 map_poses[indexPose] = {angleAxis[0 ], angleAxis[1 ], angleAxis[2 ], t (0 ), t (1 ), t (2 )}; double * parameter_block = &map_poses.at (indexPose)[0 ];problem.AddParameterBlock (parameter_block, 6 ); std::vector<int > vec_constant_extrinsic; vec_constant_extrinsic.insert (vec_constant_extrinsic.end (), {1 ,2 ,3 }); if (!vec_constant_extrinsic.empty ()) { ceres::SubsetParameterization *subset_parameterization = new ceres::SubsetParameterization (6 , vec_constant_extrinsic); problem.SetParameterization (parameter_block, subset_parameterization); }
优化相机内参及畸变系数,pose 是常量不优化和 3D landmark,代价函数写法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 template <typename CameraModel> class BundleAdjustmentConstantPoseCostFunction {public : BundleAdjustmentConstantPoseCostFunction (const Eigen::Vector4d& qvec, const Eigen::Vector3d& tvec, const Eigen::Vector2d& point2D) : qw_ (qvec (0 )), qx_ (qvec (1 )), qy_ (qvec (2 )), qz_ (qvec (3 )), tx_ (tvec (0 )), ty_ (tvec (1 )), tz_ (tvec (2 )), observed_x_ (point2D (0 )), observed_y_ (point2D (1 )) {} static ceres::CostFunction* Create (const Eigen::Vector4d& qvec, const Eigen::Vector3d& tvec, const Eigen::Vector2d& point2D) return (new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction< BundleAdjustmentConstantPoseCostFunction<CameraModel>, 2 , 3 , CameraModel::kNumParams>( new BundleAdjustmentConstantPoseCostFunction (qvec, tvec, point2D))); } template <typename T> bool operator () (const T* const point3D, const T* const camera_params, T* residuals) const const T qvec[4 ] = {T (qw_), T (qx_), T (qy_), T (qz_)}; T projection[3 ]; ceres::UnitQuaternionRotatePoint (qvec, point3D, projection); projection[0 ] += T (tx_); projection[1 ] += T (ty_); projection[2 ] += T (tz_); projection[0 ] /= projection[2 ]; projection[1 ] /= projection[2 ]; CameraModel::WorldToImage (camera_params, projection[0 ], projection[1 ], &residuals[0 ], &residuals[1 ]); residuals[0 ] -= T (observed_x_); residuals[1 ] -= T (observed_y_); return true ; } private : const double qw_; const double qx_; const double qy_; const double qz_; const double tx_; const double ty_; const double tz_; const double observed_x_; const double observed_y_; };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 ceres::Problem problem; ceres::CostFunction* cost_function = nullptr ; ceres::LossFunction * p_LossFunction = ceres_options_.bUse_loss_function_ ? new ceres::HuberLoss (Square (4.0 )) : nullptr ; cost_function = BundleAdjustmentConstantPoseCostFunction<CameraModel>::Create ( image.Qvec (), image.Tvec (), point2D.XY ()); problem_->AddResidualBlock (cost_function, loss_function, point3D.XYZ ().data (), camera_params_data);